Quickstart of WFilter 4.1
Contents |
1 Download and Decompress WFilter
Download WFilter and decompress it with WinZip. Double click the exe file to launch the installation.
You will be asked to choose file-based version or database version. There is no feature difference between the "database version" and "file-based version", except for data storage.
For first time using WFilter, you're recommended to choose the file-based version.
2 Installation Notice
Calculate hard disk space required
- Because monitored data will be kept in your disk, so you need to calculate the required disk space and choose a proper disk to install WFilter.
- Required harddisk space is related to monitored computers number and log keeping days, each monitored computer will cost about 2M space per day.
Installation of WFilter dataBase version
- If you want to install WFilter database version, you should install database first. WFilter database version supports SQL Server and MySQL database. Please refer to WFilter Database Version Guide.
3 Launching WFilter Console
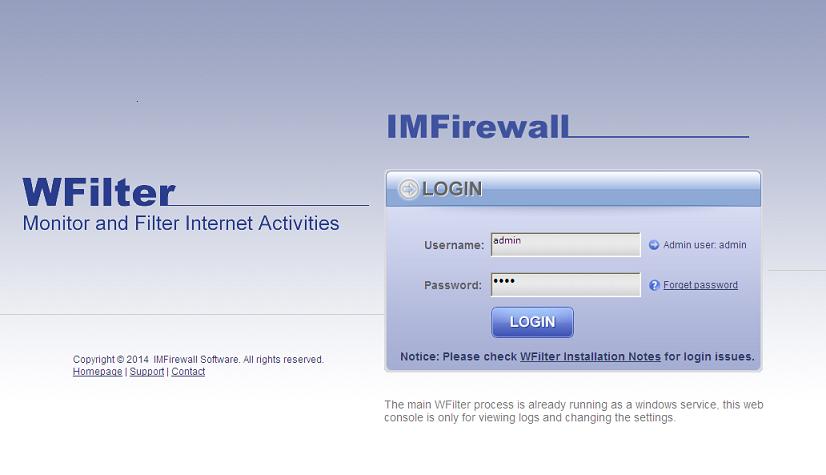
You can launch WFilter console by clicking the WFilter shortcut on desktop, or run "Start" -> "Programs" -> "IMFirewall" -> "WFilter Console". Or you can type "http://127.0.0.1:9090" in your browser address bar to access WFilter console.
The default administrator user is "admin", admin password is configured during WFilter installation.
For first time using WFilter, you will see the "Configuration Wizard", please modify certain settings following the wizard. Then you can click "online users" to check the monitored devices, as in below Figure:
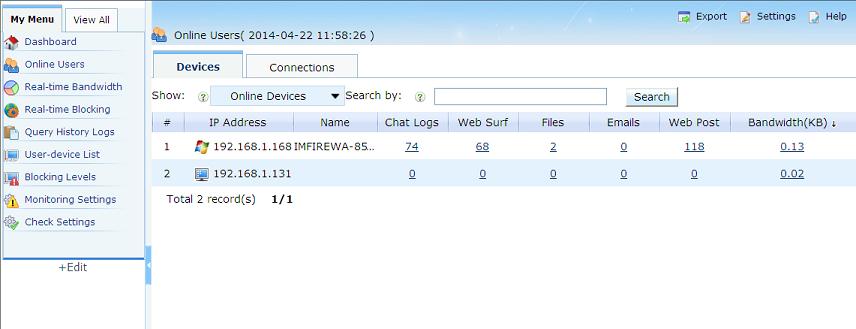
The WFilter computer must be deployed at a single location in the network where it can monitor all internet traffic. Otherwise it can not work properly.
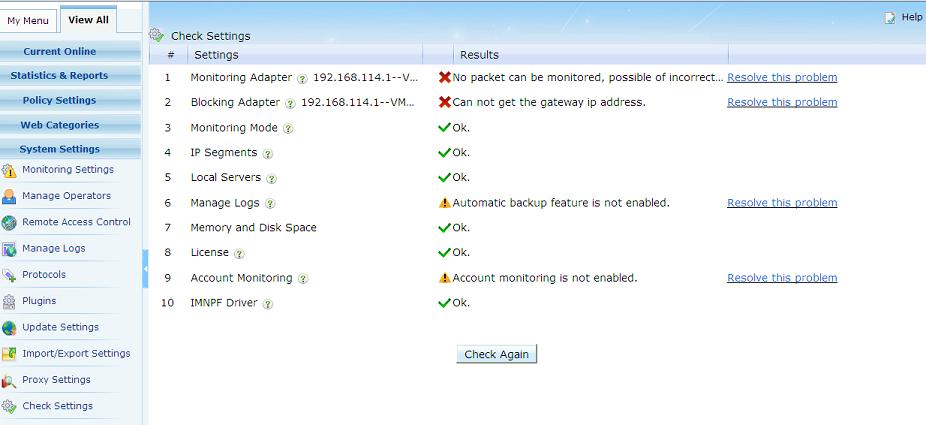
If no computer appears in "online computers", this is usually because incorrect monitoring adapter settings, please check Monitoring Settings.
If WFilter can only monitor itself, this is a deployment issue, please check "How to deploy WFilter?" for more details.
4 Configure WFilter
If no device presents in the "online users", there are two possibilities:
- You haven't have any network activity yet. Please visit some websites and refresh the "Online Users" to check.
- The monitoring adapter is configured incorrectly. As in "Figure 4.1", please run "system settings"->"check settings" to check current settings and follow the guide to fix the errors.
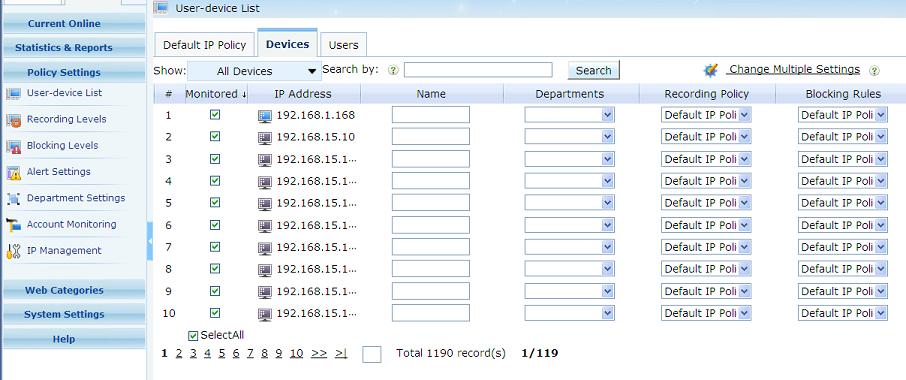
How to set internet policy for monitored computers?
- As in picture, click the "User-computer Table". Check the "Enable Monitor" checkbox of the computer you want to monitor. You also can set blocking policy for computers in this page.
5 How to deploy WFilter?
Introduction
- You only need to install WFilter in ONE computer to monitor the whole network. However, the WFilter computer must be deployed at a single location in the network where it can monitor all internet traffic.
- There are two different kinds of deployment solutions:
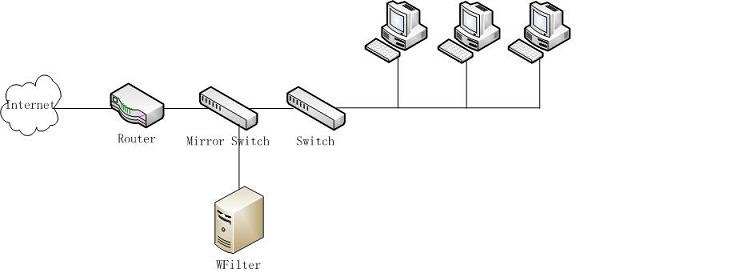
A Typical Small Network
- As in Figure 5.1, local computers use a wired router to connect to the Internet. In this type of network, it requires a port mirroring switch to be installed between the router and the switch. And the machine with WFilter installed on shall be connected to the monitor port of the port mirroring switch.
- For better understanding of WFilter deployment, please check: WFilter Deployment Examples.